How to produce the CTC?
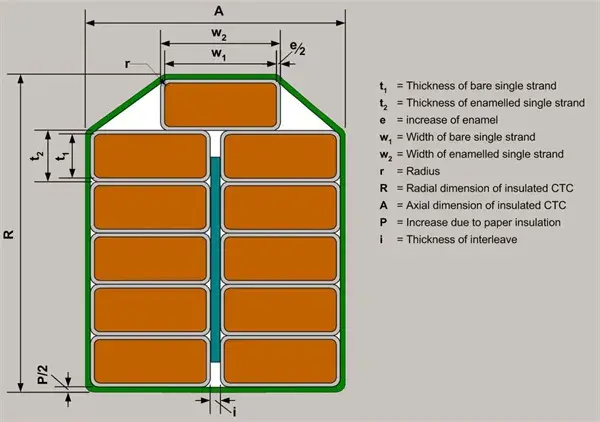
Materials and Preparation
- Selection of Conductor Material:
- Copper or aluminum strips are typically used for CTC due to their excellent electrical conductivity.
- The strips are usually rectangular in cross-section to maximize packing density and minimize losses.
- Insulation:
- Each individual strand is coated with an insulating layer, usually a thin film of enamel or another insulating material.
Manufacturing Process
- Strand Preparation:
- The conductor strips are cut to the desired length and dimensions.
- The strips are then coated with the insulating material if they are not pre-insulated.
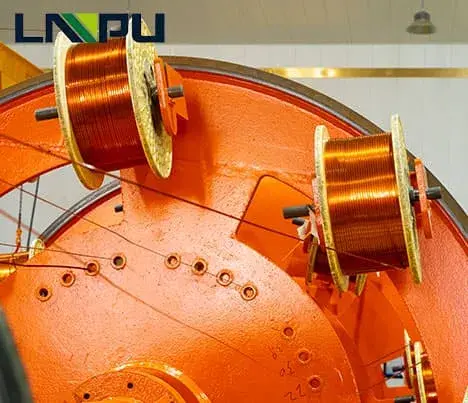
- Stranding and Stacking:
- The insulated strands are arranged in a specific pattern and stacked to form a bundle.
- The arrangement ensures that each strand is in the correct position for subsequent transposition.
- Transposition:
- The strands are continuously transposed along the length of the cable. This involves twisting and swapping the positions of the strands in a precise and regular pattern.
- This transposition ensures that each strand experiences similar electrical and magnetic environments, reducing losses due to eddy currents and circulating currents.
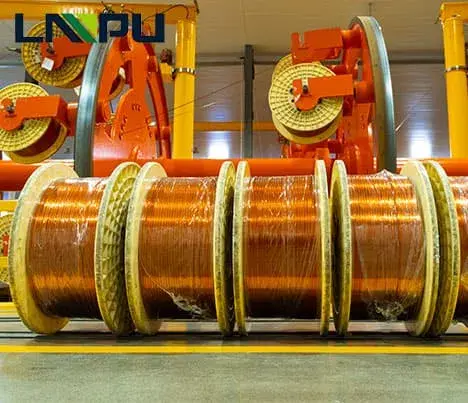
- Binding and Wrapping:
- The transposed bundle of strands is bound together using a suitable binding material.
- An additional layer of insulation is often applied to the entire bundle to provide mechanical protection and electrical isolation from other components.
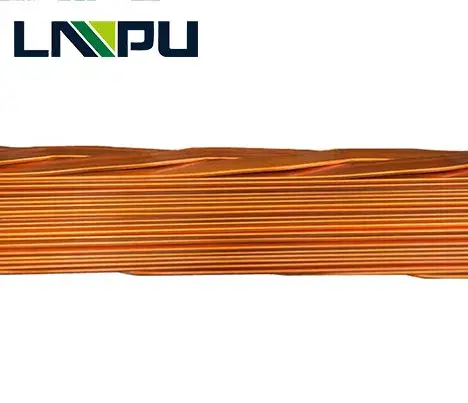
- Forming and Shaping:
- The CTC is shaped into the desired form, which could be a rectangular or oval cross-section, depending on the application.
- This shaping process ensures that the CTC fits properly into the transformer or reactor windings.
Quality Control and Testing
- Electrical Testing:
- The completed CTC is subjected to various electrical tests to ensure it meets the required conductivity and insulation specifications.
- Tests include measuring resistance, insulation integrity, and checking for continuity.
- Mechanical Testing:
- Mechanical properties such as flexibility, tensile strength, and resistance to mechanical stresses are tested.
- Ensuring that the CTC can withstand the mechanical demands of the application is crucial.
- Thermal Testing:
- Thermal performance is evaluated to ensure the CTC can operate within the desired temperature range without degradation.
Final Assembly and Packaging
- Final Inspection:
- A thorough inspection is conducted to check for any manufacturing defects or inconsistencies.
- This includes visual inspections and verification of all test results.
- Packaging:
- The finished CTC is carefully packaged to prevent damage during transportation.
- Appropriate labeling is applied to ensure traceability and proper handling instructions.